A Appendix A: Development Plan
- Algorithm incorporation
- Joint pulses
- covariates
- Population model
- covariates
- Joint pulses
- Modularization/refactoring
- Manual/webbook
- Package features
- Summary and diagnostic functions
A.1 Software map
- Single subject
- Single hormone
- 2 hormones
- Options:
- Orderstat vs Strauss
- Changing baseline??
- Population model
- Single hormone
- Single group (no covariates)
- Covariates (> 1 group)
- Choose which parameters to do as a regression (- categorical parameters; - continuous parameters), others under single group assumptions.
- 2 hormones
- Single group
- non 1-to-1 (imperfect)
- 2 driver (method needed) (what does this mean?)
- Covariates (> 1 group)
- non 1-to-1, imperfect, ???pamm done (p), need v/nu?? (what does this mean?)
- 2 driver (method needed) (what does this mean?)
- Single group
- Single hormone
A.2 Base code versions for github archiving
All variations
Major versions
- Single-subject, single hormone
- Single-subject, associational (2-hormone)
- Population model, single hormone
- Population model, covariates, single hormone
- Population model, associational (2-hormone) hormone
- Population model, covariates, associational (2-hormone) hormone
Minor versions
- Fixed baseline vs. change-point baseline vs changing baseline (sinusoidal)
- Orderstat vs. Strauss prior on pulse location
- Log-normal vs. truncated t prior on mean mass/width
- Only truncated-t going forward
- Inverse Wishart vs. half-Cauchy vs. Uniform prior on re_sd
- Only Uniform prior going forward
Questions
- Terminology: driver/response OR trigger/response
Summary and diagnostic functions
mcmc_trace <- function() {}mcmc_posteriors <- function() {}mcmc_locations <- function() {}
STAN and other Bayesian R package functions to implement
Posterior predicted values/plot
rstanarm::posterior_predict()rstanarm::ppc_dens_overlay()rstanarm::ppc_intervals()
Posterior densities
rstanarm::mcmc_areas()
#--------------------------------------------
# STAN examples
# Some examples http://mc-stan.org/bayesplot/
#--------------------------------------------
if (!require(bayesplot)) install.packages("bayesplot")## Loading required package: bayesplot## This is bayesplot version 1.4.0## - Plotting theme set to bayesplot::theme_default()## - Online documentation at mc-stan.org/bayesplotif (!require(rstanarm)) install.packages("rstanarm")## Loading required package: rstanarm## Loading required package: Rcpp## Loading required package: methods## rstanarm (Version 2.17.3, packaged: 2018-02-17 05:11:16 UTC)## - Do not expect the default priors to remain the same in future rstanarm versions.## Thus, R scripts should specify priors explicitly, even if they are just the defaults.## - For execution on a local, multicore CPU with excess RAM we recommend calling## options(mc.cores = parallel::detectCores())## - Plotting theme set to bayesplot::theme_default().if (!require(ggplot2)) install.packages("ggplot2")## Loading required package: ggplot2library(bayesplot)
library(rstanarm)
library(ggplot2)
fit <- stan_glm(mpg ~ ., data = mtcars)##
## SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'continuous' NOW (CHAIN 1).
##
## Gradient evaluation took 5.4e-05 seconds
## 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.54 seconds.
## Adjust your expectations accordingly!
##
##
## Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
##
## Elapsed Time: 0.475231 seconds (Warm-up)
## 0.391947 seconds (Sampling)
## 0.867178 seconds (Total)
##
##
## SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'continuous' NOW (CHAIN 2).
##
## Gradient evaluation took 1.7e-05 seconds
## 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.17 seconds.
## Adjust your expectations accordingly!
##
##
## Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
##
## Elapsed Time: 0.447735 seconds (Warm-up)
## 0.425246 seconds (Sampling)
## 0.872981 seconds (Total)
##
##
## SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'continuous' NOW (CHAIN 3).
##
## Gradient evaluation took 1.7e-05 seconds
## 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.17 seconds.
## Adjust your expectations accordingly!
##
##
## Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
##
## Elapsed Time: 0.435891 seconds (Warm-up)
## 0.419295 seconds (Sampling)
## 0.855186 seconds (Total)
##
##
## SAMPLING FOR MODEL 'continuous' NOW (CHAIN 4).
##
## Gradient evaluation took 1.8e-05 seconds
## 1000 transitions using 10 leapfrog steps per transition would take 0.18 seconds.
## Adjust your expectations accordingly!
##
##
## Iteration: 1 / 2000 [ 0%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 200 / 2000 [ 10%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 400 / 2000 [ 20%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 600 / 2000 [ 30%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 800 / 2000 [ 40%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1000 / 2000 [ 50%] (Warmup)
## Iteration: 1001 / 2000 [ 50%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1200 / 2000 [ 60%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1400 / 2000 [ 70%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1600 / 2000 [ 80%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 1800 / 2000 [ 90%] (Sampling)
## Iteration: 2000 / 2000 [100%] (Sampling)
##
## Elapsed Time: 0.419634 seconds (Warm-up)
## 0.385577 seconds (Sampling)
## 0.805211 seconds (Total)posterior <- as.matrix(fit)
plot_title <- ggtitle("Posterior distributions with medians and 80% intervals")
mcmc_areas(posterior, pars = c("cyl", "drat", "am", "wt"), prob = 0.8) +
plot_title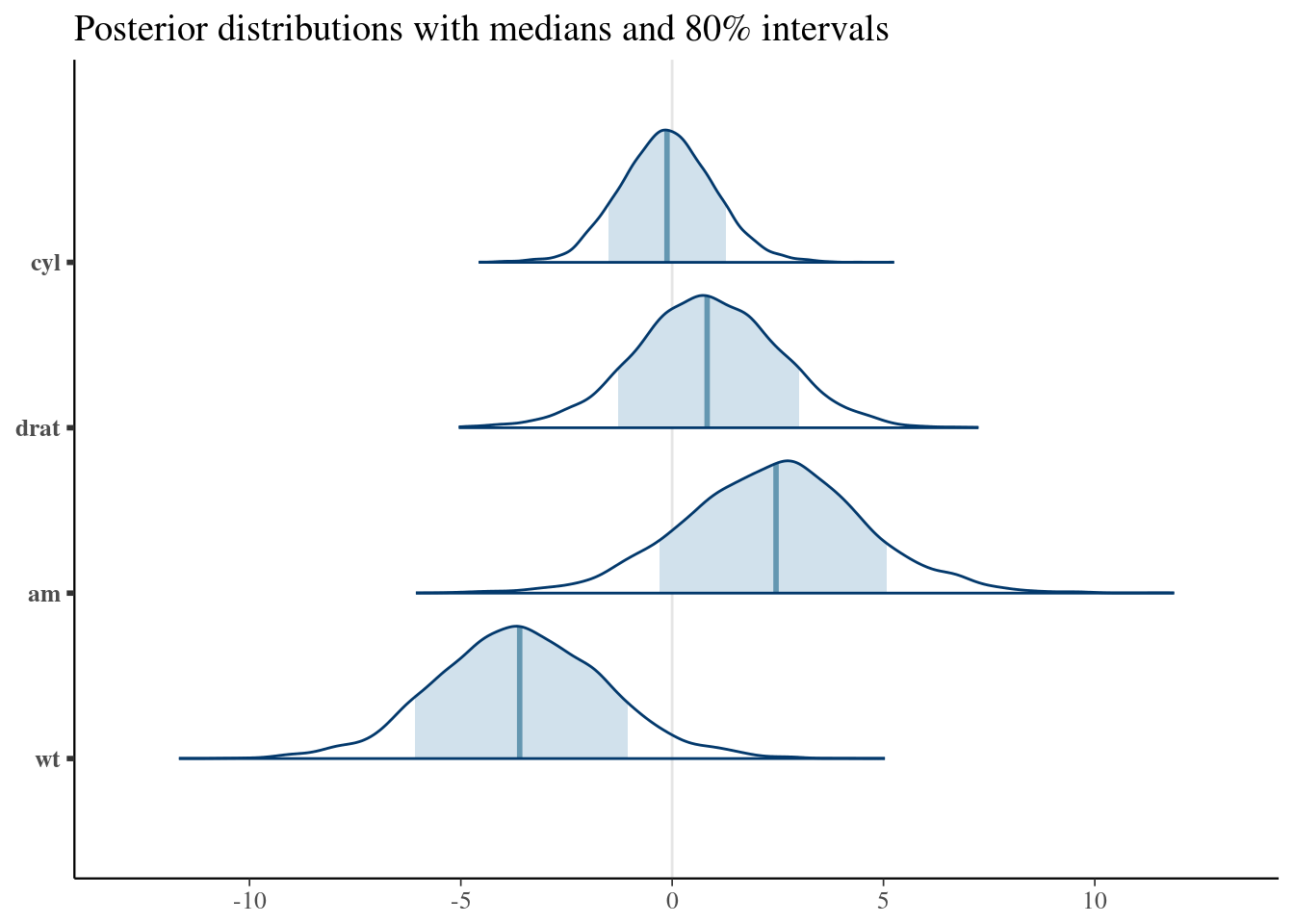
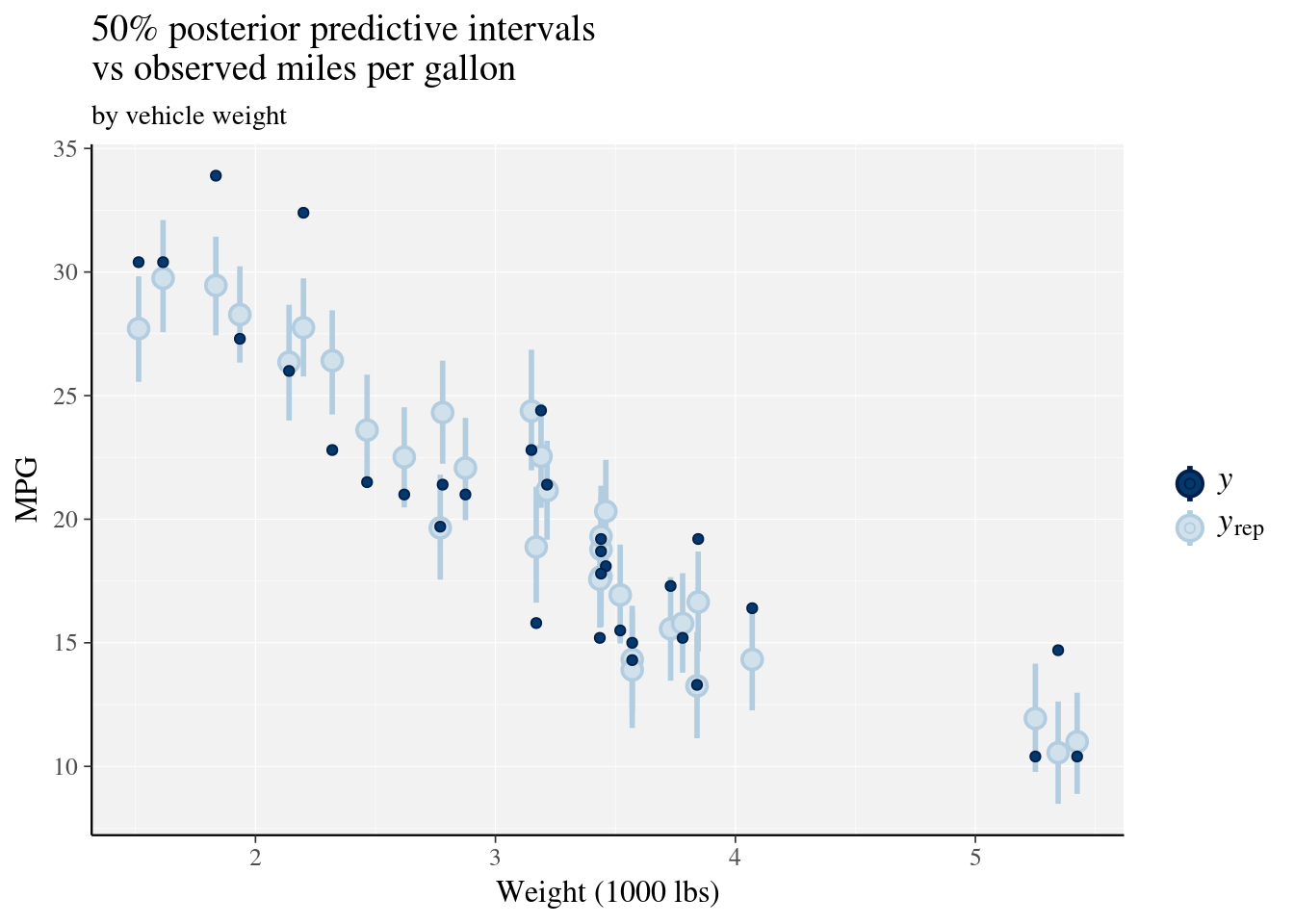
ppc_intervals(y = mtcars$mpg, yrep = posterior_predict(fit), x = mtcars$wt, prob = 0.5) +
labs(x = "Weight (1000 lbs)",
y = "MPG",
title = "50% posterior predictive intervals \nvs observed miles per gallon",
subtitle = "by vehicle weight") +
panel_bg(fill = "gray95", color = NA) +
grid_lines(color = "white")